Inorganic Chemistry Worksheets Results
Practice Problems for Naming Inorganic Compounds
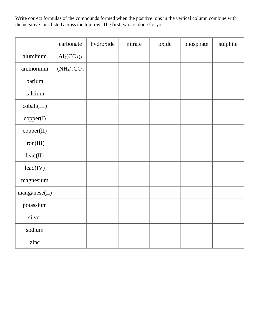
Ca(C2H3O2)2 AgCN lead(II) chlorite disulfur decafluoride cobalt(III) oxide aluminum perchlorate sodium chromate acetic acid calcium fluoride nickel(II) dichromate hydroiodic acid tin(IV) chloride diphosphorus pentaoxide sodium nitrate gold(III) iodide zinc hydrogen carbonate potassium permanganate nitrogen tribromide
https://url.theworksheets.com/2gdu653 Downloads
Preview and Download !

Inorganic Nomenclature Worksheet: Names of Coordination Compounds
Note: Nomenclature for inorganic compounds refers to the process of naming those compounds. All of the aspects that make a compound unique must be included in a comprehensive chemical name. This assignment is designed to help you develop the skill of correctly naming inorganic complexes. It will guide you through the process of identifying
https://url.theworksheets.com/6fni115 Downloads
Preview and Download !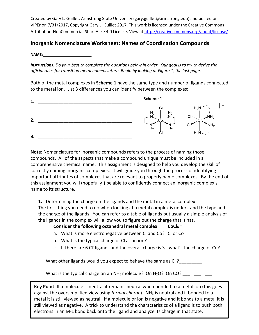
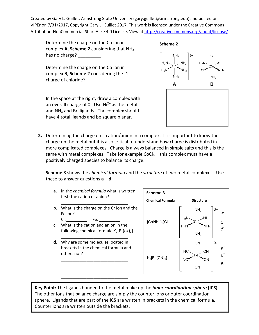

NOMENCLATURE FOR SIMPLE INORGANIC COMPOUNDS - Everett Community College
NOMENCLATURE FOR SIMPLE INORGANIC COMPOUNDS Everett Community College Tutoring Center STEPS TO FOLLOW WHEN GIVEN FORMULAS AND ASKED TO NAME THE COMPOUND: 1. Look at the formula to see if it is a binary compound i.e. only 2 elements. 2. If it is a binary compound, check to see which of the following it is: a) Metal + Non-metal
https://url.theworksheets.com/a1k132 Downloads
Preview and Download !


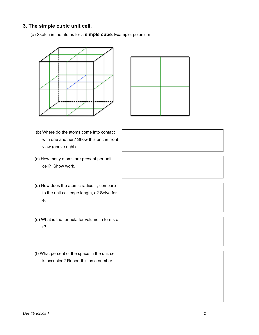
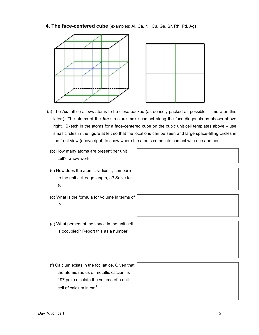
Inorganic Chemistry with Doc M. Day 10. Ionic Thrills, Part 1.
Day 10 Ionics 1 3 4. The face-centered cube (examples: Al, Ca, Ni, Cu, Ge, Sr, Rh, Pd, Ag) (a) The fcc lattice allows atoms to be close-packed (as densely packed as possible — more on this later.) The atoms of the fcc structure make contact along the face-diagonals as shown above right. Sketch in the atoms for a face-centered cube on the cubic unit cell templates above – use
https://url.theworksheets.com/2gdy149 Downloads
Preview and Download !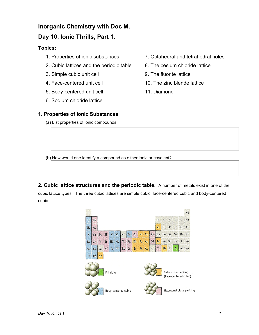
ORGANIC & INORGANIC COMPOUNDS - Minersville Area School District
Inorganic compounds are chemical compounds without carbon atoms. Identify the type of compound (Inorganic/Organic) and the major properties (salt, acid, base, protein, lipid, nucleic acid or carbohydrate) for each of the substances below. Matter Class Properties 1. Bone 2. Caramel 3. Corn oil 4. DNA 5. ...
https://url.theworksheets.com/6fnn130 Downloads
Preview and Download !


Laboratory manual Of PRACTICAL INORGANIC II CHEMISTRY - UNY
Inorganic II course. The English edition of Inorganic II laboratory work manual is the same in contents with Indonesian edition. Revision done by simplifies the language and the direction also separates the manual and the worksheet. It is hoped, this manual may be a guideline to improve student laboratory skill especially in inorganic ...
https://url.theworksheets.com/bea244 Downloads
Preview and Download !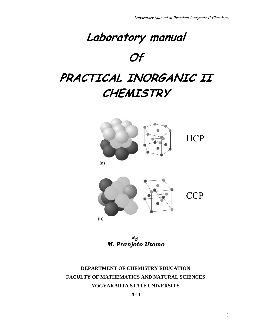


Name Date / / ORGANIC & INORGANIC COMPOUNDS - Minersville Area School ...
ORGANIC & INORGANIC COMPOUNDS Matter Bone Caramel Corn oil DNA Hair Hydrogen Chloride Maple Syrup Margarine Muscle NaOH Potassium chloride RNA Sugar Vinegar Whale Blubber Class Organic Organic Organic Organic Organic Inorganic Organic Organic Organic Inorganic Inorganic Organic Organic Inorganic
https://url.theworksheets.com/6fnq107 Downloads
Preview and Download !


Branches of Chemistry Worksheet - Leverage Edu
Branches of Chemistry Worksheet Q1. Hair contains keratin proteins which are alsopresent in nails and wool is anexample of: Biochemistry Inorganic chemistry Physical chemistry organic chemistry Q2. Branch of chemistry dealing with the plantationand overcoming greenhouse effectis: Biochemistry Organic chemistry Environmental chemistry
https://url.theworksheets.com/2gdw207 Downloads
Preview and Download !


AS-Level INORGANIC CHEMISTRY - Weebly
INORGANIC CHEMISTRY. What is the formula of the cyanate ion present in ammonium cyanate? A CNO – B CNO. 2– C CO – D NO – Q21 In which pair is the radius of the second atom greater than that of the first atom? A Na, Mg B Sr, Ca C P, N D Cl, Br Q22 The oxide and chloride of an element X are separately mixed with water. The two
https://url.theworksheets.com/5xv9108 Downloads
Preview and Download !

INORGANIC CHEMISTRY QUESTION BANK FOR BSC 1st YEAR STUDENTS - Fullonstudy
3 | P a g e 48) Size of anion is always bigger than parent atom. Explain. 49) Explain sp2 hybridization with suitable example. 50) An orbital cannot accommodate more than two electrons. Justify the statement. 51) Nitrogen is electronegative element, however its electron affinity is virtually zero. Explain? 52) Explain geometry of hydronium ion. 53) Explain the Frenkel defect of ionic crystal.
https://url.theworksheets.com/6fnt114 Downloads
Preview and Download !


Next results >>